Welcome, business owners! In today’s digital age, ensuring the cybersecurity of your enterprise is more crucial than ever. With the increasing frequency of cyber attacks and data breaches, it is essential to implement robust measures to protect your sensitive information and safeguard your operations. In this article, we will explore some key cybersecurity measures that every business should consider to secure their data and mitigate risks effectively.
Importance of Enterprise Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity has become a critical issue for enterprises of all sizes in today’s digital landscape. With the increasing frequency and sophistication of cyber attacks, organizations must prioritize their cybersecurity efforts to protect their sensitive data and confidential information. Implementing robust cybersecurity measures is not only necessary for safeguarding a company’s assets but also for maintaining the trust and confidence of customers, partners, and stakeholders.
One of the primary reasons why enterprise cybersecurity is essential is to prevent data breaches and security incidents that can have devastating consequences. A cybersecurity breach can lead to a loss of sensitive information, financial losses, damage to reputation, and legal ramifications. In some cases, a data breach can even result in the closure of a business. By investing in cybersecurity, organizations can reduce the risk of cyber attacks and defend against potential threats.
Additionally, enterprise cybersecurity is crucial for ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements and industry standards. Many industries have specific data protection regulations that companies must adhere to, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the United States. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in hefty fines and penalties. By implementing robust cybersecurity measures, organizations can ensure that they are meeting the necessary compliance standards and avoiding legal repercussions.
Furthermore, cybersecurity is essential for maintaining the trust and confidence of customers and partners. In today’s interconnected world, consumers are increasingly concerned about the security of their personal data and are more likely to do business with companies that prioritize cybersecurity. A strong cybersecurity posture can help build trust with customers, increase brand loyalty, and differentiate a company from its competitors. Similarly, partners and stakeholders will also view an organization more favorably if they know that their data is being protected effectively.
In conclusion, enterprise cybersecurity is crucial for protecting sensitive data, preventing security incidents, ensuring compliance with regulations, and maintaining trust with customers and partners. By investing in cybersecurity measures, organizations can strengthen their security posture, mitigate risks, and safeguard their assets in an increasingly digital world.
Common Cyber Threats Faced by Enterprises
Enterprises face a multitude of cyber threats on a daily basis, with hackers constantly evolving and finding new ways to breach security measures. Some of the most common cyber threats faced by enterprises include:
1. Phishing Attacks: Phishing attacks are one of the most prevalent cyber threats faced by enterprises. This type of attack involves sending fraudulent emails that appear to be from reputable sources in order to trick recipients into providing sensitive information such as login credentials or financial details. Phishing attacks can be extremely damaging as they can lead to data breaches and financial loss.
2. Ransomware: Ransomware is a type of malware that encrypts a user’s files and demands a ransom in exchange for the decryption key. Ransomware attacks can cripple an enterprise’s operations and result in significant financial losses. Hackers often deploy ransomware through phishing emails or by exploiting vulnerabilities in outdated software.
Ransomware attacks have become increasingly sophisticated in recent years, with hackers targeting high-profile enterprises and demanding larger ransom payments. Enterprises must implement robust cybersecurity measures such as regular data backups, employee training, and network segmentation to protect against ransomware attacks.
3. Insider Threats: Insider threats occur when current or former employees misuse their access to sensitive information for malicious purposes. This can include intentionally leaking confidential data, stealing intellectual property, or installing malware on company systems. Insider threats are difficult to detect as the perpetrators often have legitimate access to the organization’s network.
To mitigate insider threats, enterprises should implement strong access controls, conduct regular security training for employees, and monitor user activity on their network. By closely monitoring user behavior and implementing strict security protocols, enterprises can reduce the risk of insider threats.
4. DDoS Attacks: Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks are another common cyber threat faced by enterprises. These attacks involve flooding a target website or network with an overwhelming amount of traffic, causing it to become slow or completely inaccessible. DDoS attacks can disrupt business operations, damage reputations, and result in financial losses.
Enterprises can protect against DDoS attacks by investing in DDoS mitigation services, implementing firewalls and intrusion prevention systems, and establishing a response plan in the event of an attack. By proactively defending against DDoS attacks, enterprises can ensure the continued availability of their online services.
5. Malware: Malware refers to malicious software designed to infiltrate systems and steal sensitive information. Common types of malware include viruses, worms, Trojans, and spyware. Malware can enter an enterprise’s network through infected email attachments, software downloads, or malicious websites.
Enterprises can defend against malware by regularly updating antivirus software, conducting security awareness training for employees, and implementing proactive security measures such as intrusion detection systems. By staying vigilant and adopting a multi-layered approach to cybersecurity, enterprises can minimize the risk of malware infections.
Best Practices for Enterprise Cybersecurity
When it comes to keeping your company’s data safe from cyber threats, it’s essential to have strong cybersecurity practices in place. Here are some best practices that enterprises should follow to ensure the security of their data:
1. Implement a Strong Firewall: One of the first lines of defense against cyber attacks is a strong firewall. Make sure your enterprise has a robust firewall in place that can filter out potentially harmful traffic and protect your network from unauthorized access.
2. Regularly Update Software: Keeping your software up to date is crucial for protecting your systems from vulnerabilities that cyber attackers could exploit. Make sure that all software, including operating systems, antivirus programs, and applications, are regularly updated with the latest security patches.
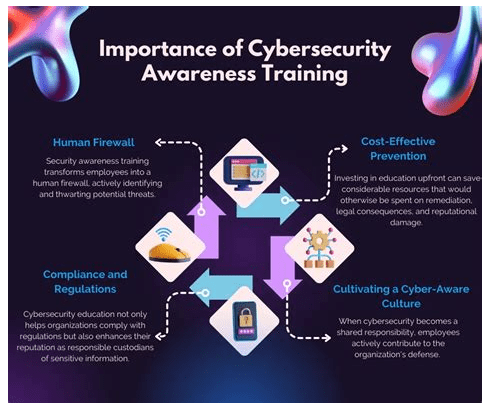
3. Train Employees on Cybersecurity Awareness: One of the weakest links in enterprise cybersecurity is often employees who may inadvertently click on malicious links or download infected files. It is essential to educate employees on cybersecurity awareness regularly. This training should cover topics such as recognizing phishing emails, creating strong passwords, and avoiding suspicious websites. Conducting simulated phishing attacks can also help identify employees who may need additional training.
4. Implement Strong Access Controls: Limiting access to sensitive data is critical for protecting it from unauthorized users. Implement strong access controls that only allow employees to access the information they need to perform their jobs. Regularly review and update access permissions to ensure that former employees no longer have access to company data.
5. Encrypt Data: Encrypting data ensures that even if cyber attackers manage to access it, they won’t be able to read it without the encryption key. Implement encryption for sensitive data both in transit and at rest to protect it from unauthorized access.
6. Backup Data Regularly: In the event of a cyber attack or data breach, having backups of your data is crucial for recovery. Regularly back up your data and store it securely either offline or in the cloud. Test your backups regularly to ensure that you can quickly restore your data if needed.
7. Monitor Network Activity: Monitoring network activity can help you detect any unusual or suspicious behavior that could signal a cyber attack. Implement network monitoring tools that track traffic patterns, monitor for anomalies, and provide alerts for potential security threats.
8. Develop an Incident Response Plan: Despite your best efforts to prevent cyber attacks, it’s essential to have a plan in place for responding to a security incident. Develop an incident response plan that outlines the steps to take in the event of a breach, including who to contact, how to contain the breach, and how to recover your systems.
By following these best practices for enterprise cybersecurity, you can better protect your company’s data from cyber threats and minimize the risk of a security breach. Remember that cybersecurity is an ongoing process, and staying vigilant in the face of evolving threats is key to keeping your data safe.
Role of Employees in Ensuring Cybersecurity
Employees play a vital role in ensuring cybersecurity within an enterprise. They are the front line of defense against cyber threats and are responsible for following security protocols to protect sensitive information and data. One of the key ways employees can contribute to cybersecurity is through awareness and training. By educating employees on the latest cyber threats, best practices for securing data, and how to identify malicious activities, organizations can empower their workforce to be proactive in preventing cyber attacks.
Furthermore, employees are responsible for implementing security measures such as using strong passwords, enabling two-factor authentication, and updating software regularly. These basic security practices may seem simple, but they are essential in protecting a company’s network and data from cyber threats. Employees also play a crucial role in maintaining a secure work environment by being vigilant for suspicious emails, websites, or activities that could potentially compromise security.
Another important aspect of employee involvement in cybersecurity is fostering a culture of security within the organization. This includes promoting a sense of responsibility and accountability among employees for protecting sensitive information and adhering to security policies. By creating a culture where cybersecurity is a top priority, organizations can instill a mindset of vigilance and compliance among employees.
It is also essential for employees to report any security incidents or suspicious activities promptly. This includes notifying the IT department or security team of any unusual behavior or potential security breaches. By acting quickly and decisively, employees can help minimize the impact of cyber attacks and prevent further damage to the organization.
In addition to following security protocols and best practices, employees can also contribute to cybersecurity by staying informed about the latest trends and developments in the field. By staying up-to-date on emerging threats, new technologies, and industry best practices, employees can better protect themselves and their organization from potential cyber attacks.
In conclusion, the role of employees in ensuring cybersecurity within an enterprise cannot be overstated. By being aware, proactive, and vigilant in their efforts to protect sensitive information and data, employees can help safeguard their organization against cyber threats. With the right training, support, and resources, employees can play a significant role in creating a secure and resilient cybersecurity posture for their organization.
Implementing a Comprehensive Cybersecurity Strategy in Enterprises
Ensuring the security of an enterprise’s digital assets has become increasingly crucial in today’s fast-paced technological landscape. Implementing a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy is essential in protecting sensitive data, preventing cyber attacks, and maintaining the trust of customers and partners. Below are some key steps that enterprises can take to enhance their cybersecurity measures:
1. Conduct a thorough risk assessment: Before implementing any cybersecurity measures, it is important for enterprises to understand the potential risks they face. Conducting a comprehensive risk assessment can help identify vulnerabilities in network systems, applications, and data storage. This information is crucial in developing a cybersecurity strategy that addresses specific threats and vulnerabilities.
2. Invest in employee training: Employees are often the weakest link in cybersecurity, as they may unknowingly click on malicious links or download infected files. Investing in regular cybersecurity training for employees can help raise awareness about common threats and best practices for protecting sensitive information. Training sessions can cover topics such as phishing scams, password security, and how to recognize suspicious activity.
3. Implement strong access controls: Limiting access to sensitive data is key in preventing unauthorized individuals from gaining entry to critical systems. Enterprises should implement strong access controls, such as multi-factor authentication and role-based access controls, to ensure that only authorized users can access sensitive information. Regularly updating access permissions and conducting audits can help identify any unauthorized access attempts.
4. Use advanced security tools: Enterprises should invest in advanced security tools to detect, prevent, and respond to cyber threats. These tools can include firewalls, intrusion detection systems, antivirus software, and encryption technologies. By utilizing a combination of security tools, enterprises can create multiple layers of defense against potential threats.
5. Regularly update and patch systems: One of the most common ways that cyber attackers gain access to enterprise networks is through unpatched software vulnerabilities. It is crucial for enterprises to regularly update and patch all systems, applications, and devices to address known security flaws. Failure to do so can leave systems vulnerable to attacks and compromise the overall cybersecurity posture of the enterprise.
By implementing a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy that includes conducting risk assessments, investing in employee training, implementing strong access controls, using advanced security tools, and regularly updating and patching systems, enterprises can significantly enhance their cybersecurity measures. Taking proactive steps to protect digital assets can help prevent costly data breaches and maintain the trust of customers and partners.
Originally posted 2025-04-16 04:00:00.